系统结构框图
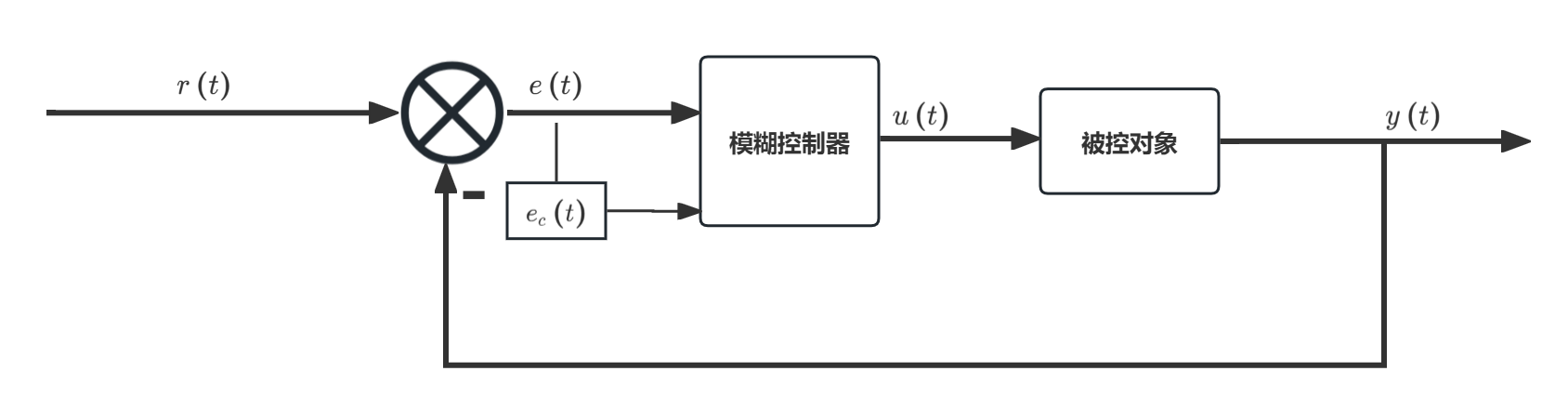
被控对象为:\frac{1}{\left( 100s+1 \right) \left( 205s+1 \right)}
模糊变量定义及论域
隶属度函数
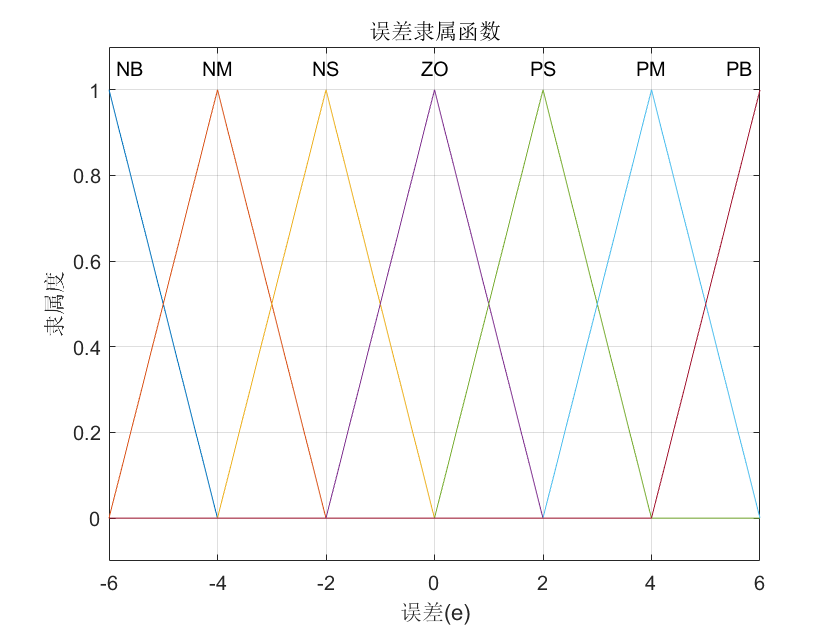
误差 e 的隶属度函数(论域:[-6, 6])
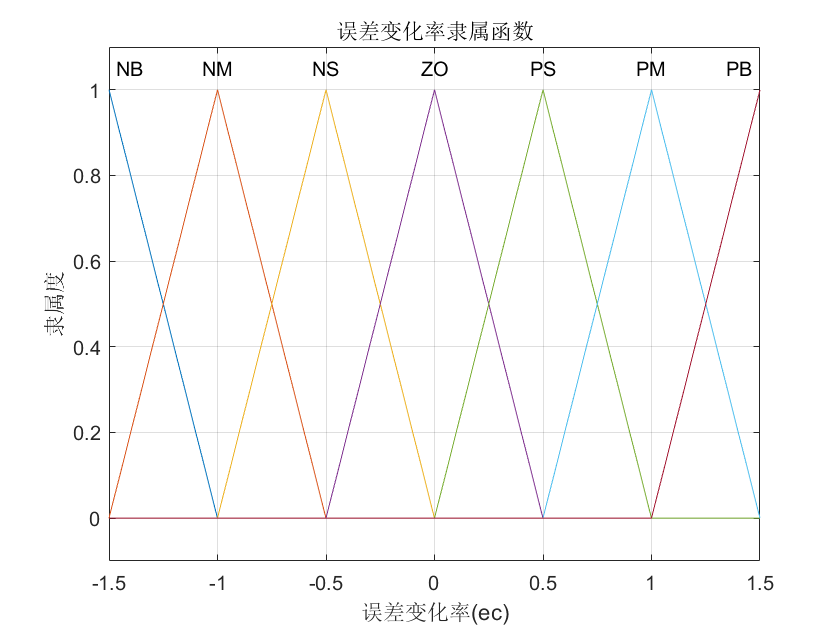
误差变化率 ec 的隶属度函数(论域:[-1.5, 1.5])
控制量 u 的隶属度函数(论域:[-15, 15])
采用三角形隶属函数实现精确量的模糊化。
图一:误差隶属度函数
图二:误差变化率隶属度函数
图三:控制输出隶属度函数
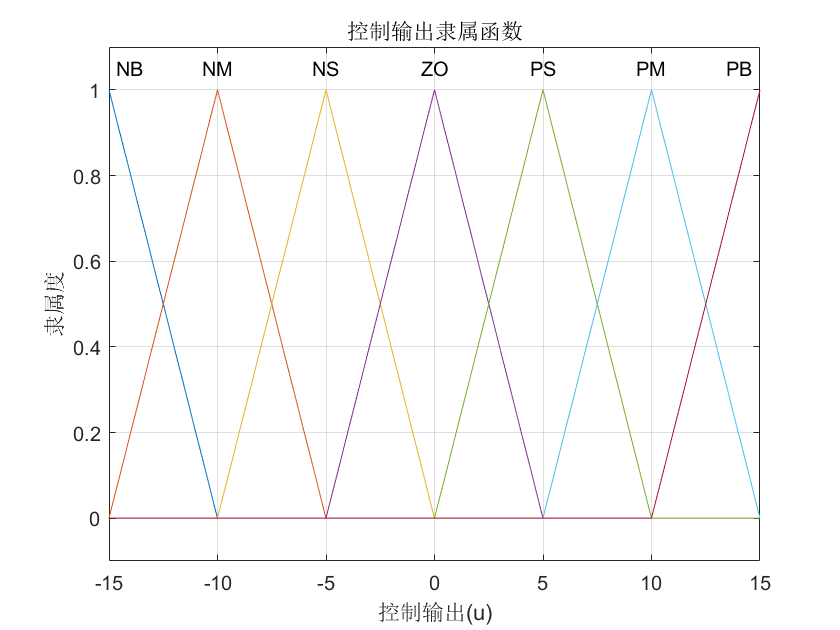
表1:输入输出变量模糊集定义
隶属度函数赋值表
表2:误差e的隶属度函数(论域:{-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3})
表3:误差变化ec的隶属度函数(论域:{-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3})
表4:控制量u的隶属度函数(论域:{-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3})
模糊控制规则表
模糊规则
第1组规则(e = NB)
Rule1: If (e is NB) and (ec is NB) then (u is PB) (1)
Rule2: If (e is NB) and (ec is NM) then (u is PB) (1)
Rule3: If (e is NB) and (ec is NS) then (u is PM) (1)
Rule4: If (e is NB) and (ec is ZO) then (u is PM) (1)
Rule5: If (e is NB) and (ec is PS) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule6: If (e is NB) and (ec is PM) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule7: If (e is NB) and (ec is PB) then (u is ZO) (1)
第2组规则(e = NM)
Rule8: If (e is NM) and (ec is NB) then (u is PB) (1)
Rule9: If (e is NM) and (ec is NM) then (u is PM) (1)
Rule10: If (e is NM) and (ec is NS) then (u is PM) (1)
Rule11: If (e is NM) and (ec is ZO) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule12: If (e is NM) and (ec is PS) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule13: If (e is NM) and (ec is PM) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule14: If (e is NM) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
第3组规则(e = NS)
Rule15: If (e is NS) and (ec is NB) then (u is PM) (1)
Rule16: If (e is NS) and (ec is NM) then (u is PM) (1)
Rule17: If (e is NS) and (ec is NS) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule18: If (e is NS) and (ec is ZO) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule19: If (e is NS) and (ec is PS) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule20: If (e is NS) and (ec is PM) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule21: If (e is NS) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
第4组规则(e = ZO)
Rule22: If (e is ZO) and (ec is NB) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule23: If (e is ZO) and (ec is NM) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule24: If (e is ZO) and (ec is NS) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule25: If (e is ZO) and (ec is ZO) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule26: If (e is ZO) and (ec is PS) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule27: If (e is ZO) and (ec is PM) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule28: If (e is ZO) and (ec is PB) then (u is NS) (1)
第5组规则(e = PS)
Rule29: If (e is PS) and (ec is NB) then (u is PS) (1)
Rule30: If (e is PS) and (ec is NM) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule31: If (e is PS) and (ec is NS) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule32: If (e is PS) and (ec is ZO) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule33: If (e is PS) and (ec is PS) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule34: If (e is PS) and (ec is PM) then (u is NM) (1)
Rule35: If (e is PS) and (ec is PB) then (u is NM) (1)
第6组规则(e = PM)
Rule36: If (e is PM) and (ec is NB) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule37: If (e is PM) and (ec is NM) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule38: If (e is PM) and (ec is NS) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule39: If (e is PM) and (ec is ZO) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule40: If (e is PM) and (ec is PS) then (u is NM) (1)
Rule41: If (e is PM) and (ec is PM) then (u is NM) (1)
Rule42: If (e is PM) and (ec is PB) then (u is NB) (1)
第7组规则(e = PB)
Rule43: If (e is PB) and (ec is NB) then (u is ZO) (1)
Rule44: If (e is PB) and (ec is NM) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule45: If (e is PB) and (ec is NS) then (u is NS) (1)
Rule46: If (e is PB) and (ec is ZO) then (u is NM) (1)
Rule47: If (e is PB) and (ec is PS) then (u is NM) (1)
Rule48: If (e is PB) and (ec is PM) then (u is NB) (1)
Rule49: If (e is PB) and (ec is PB) then (u is NB) (1)
表5:模糊控制规则表(e × ec → u)
程序设计
clear; % 清除工作区变量
close; % 关闭所有图形窗口
clc; % 清空命令窗口
%% 系统模型参数
% 定义被控对象的传递函数:G(s) = 1/((100s+1)(205s+1))
num = 1; % 分子多项式系数
den = conv([100 1], [205 1]); % 分母多项式系数,通过卷积计算(100s+1)(205s+1)
% 将传递函数转换为状态空间模型
% A: 状态矩阵, B: 输入矩阵, C: 输出矩阵, D: 直接传递矩阵
[A, B, C, D] = tf2ss(num, den);
%% 模糊控制器设计 -7个隶属度函数
% 创建Mamdani型模糊推理系统
a = mamfis('Name', '模糊控制器');
% 输入变量 e (误差)
f1 = 2.0; % 误差的缩放因子,用于调整输入变量的论域范围
% 添加输入变量e,论域范围为[-6, 6] (因为3*f1=6)
a = addInput(a, [-3*f1, 3*f1], 'Name', 'e');
% 为误差变量e添加7个三角形隶属度函数,覆盖负大(NB)到正大(PB)的范围
% trimf函数的三个参数分别定义三角形的左顶点、顶点、右顶点
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [-3*f1, -3*f1, -2*f1], 'Name', 'NB'); % 负大
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [-3*f1, -2*f1, -1*f1], 'Name', 'NM'); % 负中
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [-2*f1, -1*f1, 0], 'Name', 'NS'); % 负小
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [-1*f1, 0, 1*f1], 'Name', 'ZO'); % 零
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [0, 1*f1, 2*f1], 'Name', 'PS'); % 正小
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [1*f1, 2*f1, 3*f1], 'Name', 'PM'); % 正中
a = addMF(a, 'e', 'trimf', [2*f1, 3*f1, 3*f1], 'Name', 'PB'); % 正大
% 输入变量 ec (误差变化率)
f2 = 0.5; % 误差变化率的缩放因子
% 添加输入变量ec,论域范围为[-1.5, 1.5]
a = addInput(a, [-3*f2, 3*f2], 'Name', 'ec');
% 为误差变化率变量ec添加7个三角形隶属度函数
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [-3*f2, -3*f2, -2*f2], 'Name', 'NB'); % 负大
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [-3*f2, -2*f2, -1*f2], 'Name', 'NM'); % 负中
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [-2*f2, -1*f2, 0], 'Name', 'NS'); % 负小
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [-1*f2, 0, 1*f2], 'Name', 'ZO'); % 零
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [0, 1*f2, 2*f2], 'Name', 'PS'); % 正小
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [1*f2, 2*f2, 3*f2], 'Name', 'PM'); % 正中
a = addMF(a, 'ec', 'trimf', [2*f2, 3*f2, 3*f2], 'Name', 'PB'); % 正大
% 输出变量 u (控制量)
f3 = 5; % 控制输出的缩放因子
% 添加输出变量u,论域范围为[-15, 15]
a = addOutput(a, [-3*f3, 3*f3], 'Name', 'u');
% 为控制输出变量u添加7个三角形隶属度函数
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [-3*f3, -3*f3, -2*f3], 'Name', 'NB'); % 负大
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [-3*f3, -2*f3, -1*f3], 'Name', 'NM'); % 负中
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [-2*f3, -1*f3, 0], 'Name', 'NS'); % 负小
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [-1*f3, 0, 1*f3], 'Name', 'ZO'); % 零
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [0, 1*f3, 2*f3], 'Name', 'PS'); % 正小
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [1*f3, 2*f3, 3*f3], 'Name', 'PM'); % 正中
a = addMF(a, 'u', 'trimf', [2*f3, 3*f3, 3*f3], 'Name', 'PB'); % 正大
% 模糊规则 - 使用字符数组格式
% 基于误差(e)和误差变化率(ec)的49条模糊规则
% 规则格式:'输入条件 => 输出结论'
% 规则设计原则:当误差大时采用强控制,误差小时采用弱控制
rules = [
'e==NB & ec==NB => u=PB' % 误差负大且误差变化率负大 => 控制量正大
'e==NB & ec==NM => u=PB' % 误差负大且误差变化率负中 => 控制量正大
'e==NB & ec==NS => u=PM' % 误差负大且误差变化率负小 => 控制量正中
'e==NB & ec==ZO => u=PM' % 误差负大且误差变化率零 => 控制量正中
'e==NB & ec==PS => u=PS' % 误差负大且误差变化率正小 => 控制量正小
'e==NB & ec==PM => u=ZO' % 误差负大且误差变化率正中 => 控制量零
'e==NB & ec==PB => u=ZO' % 误差负大且误差变化率正大 => 控制量零
'e==NM & ec==NB => u=PB' % 误差负中且误差变化率负大 => 控制量正大
'e==NM & ec==NM => u=PM' % 误差负中且误差变化率负中 => 控制量正中
'e==NM & ec==NS => u=PM' % 误差负中且误差变化率负小 => 控制量正中
'e==NM & ec==ZO => u=PS' % 误差负中且误差变化率零 => 控制量正小
'e==NM & ec==PS => u=PS' % 误差负中且误差变化率正小 => 控制量正小
'e==NM & ec==PM => u=ZO' % 误差负中且误差变化率正中 => 控制量零
'e==NM & ec==PB => u=NS' % 误差负中且误差变化率正大 => 控制量负小
'e==NS & ec==NB => u=PM' % 误差负小且误差变化率负大 => 控制量正中
'e==NS & ec==NM => u=PM' % 误差负小且误差变化率负中 => 控制量正中
'e==NS & ec==NS => u=PS' % 误差负小且误差变化率负小 => 控制量正小
'e==NS & ec==ZO => u=PS' % 误差负小且误差变化率零 => 控制量正小
'e==NS & ec==PS => u=ZO' % 误差负小且误差变化率正小 => 控制量零
'e==NS & ec==PM => u=NS' % 误差负小且误差变化率正中 => 控制量负小
'e==NS & ec==PB => u=NS' % 误差负小且误差变化率正大 => 控制量负小
'e==ZO & ec==NB => u=PS' % 误差零且误差变化率负大 => 控制量正小
'e==ZO & ec==NM => u=PS' % 误差零且误差变化率负中 => 控制量正小
'e==ZO & ec==NS => u=ZO' % 误差零且误差变化率负小 => 控制量零
'e==ZO & ec==ZO => u=ZO' % 误差零且误差变化率零 => 控制量零
'e==ZO & ec==PS => u=ZO' % 误差零且误差变化率正小 => 控制量零
'e==ZO & ec==PM => u=NS' % 误差零且误差变化率正中 => 控制量负小
'e==ZO & ec==PB => u=NS' % 误差零且误差变化率正大 => 控制量负小
'e==PS & ec==NB => u=PS' % 误差正小且误差变化率负大 => 控制量正小
'e==PS & ec==NM => u=ZO' % 误差正小且误差变化率负中 => 控制量零
'e==PS & ec==NS => u=ZO' % 误差正小且误差变化率负小 => 控制量零
'e==PS & ec==ZO => u=NS' % 误差正小且误差变化率零 => 控制量负小
'e==PS & ec==PS => u=NS' % 误差正小且误差变化率正小 => 控制量负小
'e==PS & ec==PM => u=NM' % 误差正小且误差变化率正中 => 控制量负中
'e==PS & ec==PB => u=NM' % 误差正小且误差变化率正大 => 控制量负中
'e==PM & ec==NB => u=ZO' % 误差正中且误差变化率负大 => 控制量零
'e==PM & ec==NM => u=ZO' % 误差正中且误差变化率负中 => 控制量零
'e==PM & ec==NS => u=NS' % 误差正中且误差变化率负小 => 控制量负小
'e==PM & ec==ZO => u=NS' % 误差正中且误差变化率零 => 控制量负小
'e==PM & ec==PS => u=NM' % 误差正中且误差变化率正小 => 控制量负中
'e==PM & ec==PM => u=NM' % 误差正中且误差变化率正中 => 控制量负中
'e==PM & ec==PB => u=NB' % 误差正中且误差变化率正大 => 控制量负大
'e==PB & ec==NB => u=ZO' % 误差正大且误差变化率负大 => 控制量零
'e==PB & ec==NM => u=NS' % 误差正大且误差变化率负中 => 控制量负小
'e==PB & ec==NS => u=NS' % 误差正大且误差变化率负小 => 控制量负小
'e==PB & ec==ZO => u=NM' % 误差正大且误差变化率零 => 控制量负中
'e==PB & ec==PS => u=NM' % 误差正大且误差变化率正小 => 控制量负中
'e==PB & ec==PM => u=NB' % 误差正大且误差变化率正中 => 控制量负大
'e==PB & ec==PB => u=NB' % 误差正大且误差变化率正大 => 控制量负大
];
% 将规则添加到模糊推理系统
a = addRule(a, rules);
% 设置解模糊方法为重心法(centroid)
a.DefuzzificationMethod = 'centroid';
%% 系统仿真
% 定义仿真时间参数
t = 0:0.1:100; % 时间向量,从0到100秒,步长0.1秒
y = zeros(size(t)); % 初始化系统输出数组
ut = zeros(size(t)); % 初始化控制信号数组
e = zeros(size(t)); % 初始化误差数组
ec = zeros(size(t)); % 初始化误差变化率数组
x = [0; 0]; % 初始化系统状态向量[x1; x2]
% 定义控制量饱和限制
max_u = 15; % 控制量上限
min_u = -15; % 控制量下限
% 开始仿真循环
for k = 1:length(t)
% 生成参考信号:0.5*sin(0.2*t),幅值0.5,频率0.2rad/s
ref = 0.5 * sin(0.2 * t(k));
% 计算当前时刻的跟踪误差:参考信号 - 系统输出
e(k) = ref - y(k);
% 计算误差变化率(微分)
if k == 1
ec(k) = 0; % 第一个时刻的误差变化率为0
else
% 使用后向差分法计算误差变化率:de/dt ≈ (e(k)-e(k-1))/Δt
ec(k) = (e(k) - e(k-1)) / 0.1;
end
% 对输入变量进行限幅处理,确保在模糊控制器的论域范围内
e_c = max(min(e(k), 3*f1), -3*f1); % 误差限幅到[-6, 6]
ec_c = max(min(ec(k), 3*f2), -3*f2); % 误差变化率限幅到[-1.5, 1.5]
% 调用模糊推理系统计算控制量
ut_temp = evalfis(a, [e_c, ec_c]);
% 对控制量进行饱和限制,防止控制量过大
ut(k) = max(min(ut_temp, max_u), min_u);
% 系统状态更新(使用欧拉法进行数值积分)
% 计算状态导数:dx/dt = A*x + B*u
x_dot = A * x + B * ut(k);
% 更新状态:x(k+1) = x(k) + dx/dt * Δt
x = x + x_dot * 0.1;
% 计算系统输出:y = C*x + D*u
y(k) = C * x + D * ut(k);
end
%% 结果可视化
% 图1:显示误差变量的隶属函数
figure(1);
plotmf(a, 'input', 1); % 绘制第一个输入变量(e)的隶属函数
title('误差隶属函数');
xlabel('误差(e)');
ylabel('隶属度');
grid on;
% 图2:显示误差变化率变量的隶属函数
figure(2);
plotmf(a, 'input', 2); % 绘制第二个输入变量(ec)的隶属函数
title('误差变化率隶属函数');
xlabel('误差变化率(ec)');
ylabel('隶属度');
grid on;
% 图3:显示控制输出变量的隶属函数
figure(3);
plotmf(a, 'output', 1); % 绘制输出变量(u)的隶属函数
title('控制输出隶属函数');
xlabel('控制输出(u)');
ylabel('隶属度');
grid on;
% 图4:显示系统跟踪性能
figure(4);
ref_sig = 0.5 * sin(0.2 * t); % 重新生成参考信号用于绘图
plot(t, ref_sig, 'r--', t, y, 'b-'); % 红色虚线:参考信号,蓝色实线:系统输出
legend('参考信号', '系统输出');
title('位置跟踪性能');
xlabel('时间(秒)');
ylabel('位置');
grid on;
% 图5:显示控制信号
figure(5);
plot(t, ut, 'g-'); % 绿色实线:控制信号
title('控制信号');
xlabel('时间(秒)');
ylabel('控制量 u');
grid on;
% 图6:显示跟踪误差
figure(6);
plot(t, e, 'm-'); % 洋红色实线:跟踪误差
title('跟踪误差');
xlabel('时间(秒)');
ylabel('误差 e');
grid on;
% 程序结束图4:系统跟踪性能
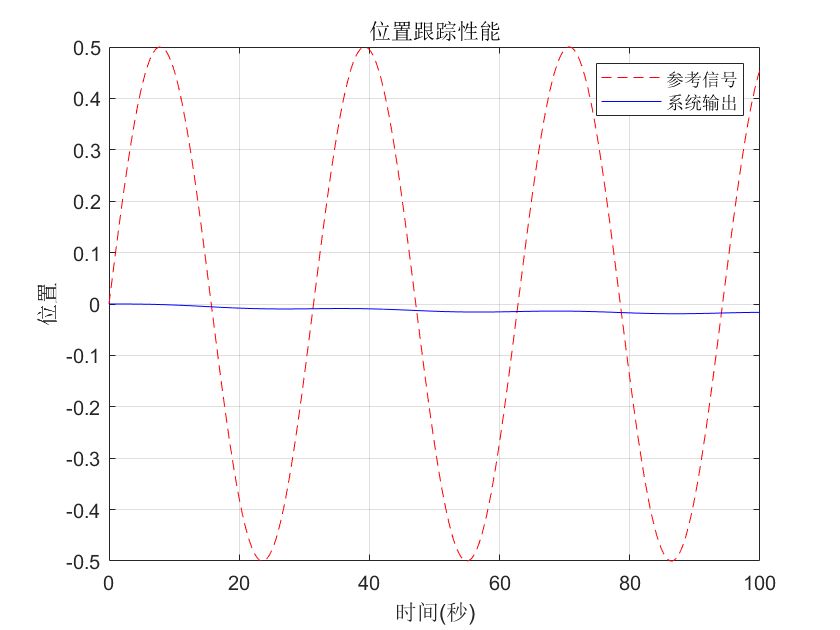
图5: 控制信号
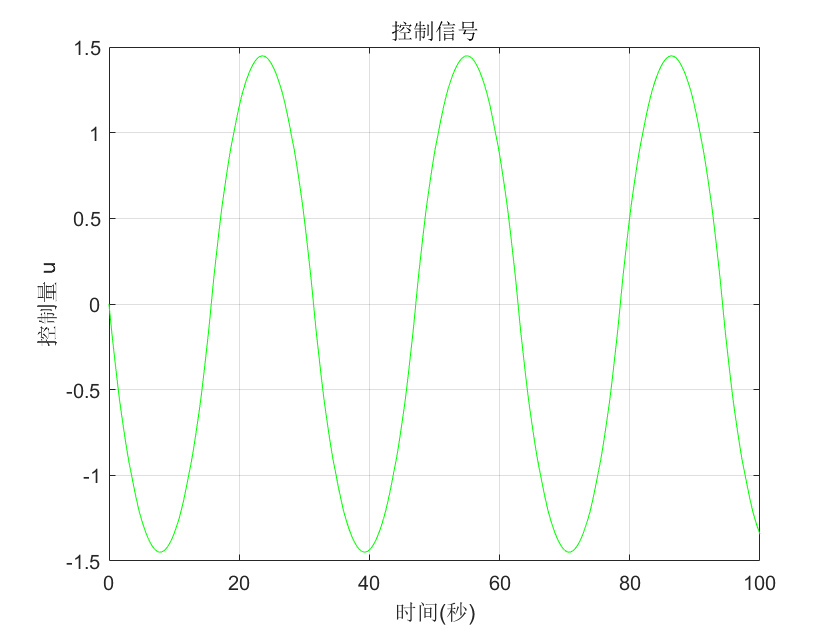
图6:跟踪误差

